At some point in time, we may hear about virtual dom, fiber, Reconciliation algorithm in react. But ever think about how this thinks works in react and why they used these things. If you did a website with HTML, CSS, and js we may have to use the ‘document.innerHTML code like this. So why don’t react can use this code instead of this crazy algorithm?
For that, we must know the basics of how the browsers work. We will not be looking into deep on this topic but a little bit to understand react challenges.
When you give an HTML page to render in the browser will get all the HTML code and its associated CSS styling. Then it will create a DOM then it will make a layout according to the CSS style and devices width and render this UI to the screen. This render needs to works like 60fps or every 60ms. If you are building a webpage with so many div then it will be a huge task for the browser to handle that page.
We can explain more about browser working in another post.
In the case of building a website using react you are not only creating a UI like we mention above we need network call back and there is so much logic that needs to be handled. That why manipulating the UI update directly to the DOM is not a good thing. It can block your code and animation become not smooth at all, slow website loading. So we need another alternative to handle these issues this is where the virtual dom comes to play.
A virtual dom is an object with a tree node. When we code a jsx like
<div className="App">
<header className="App-header">
<img src={logo} className="App-logo" alt="logo" />
<p>
</p>
<a
className="App-link"
href="https://reactjs.org"
target="_blank"
rel="noopener noreferrer"
>
Learn React
</a>
</header>
</div>
The React will create a tree with the node as each tag.
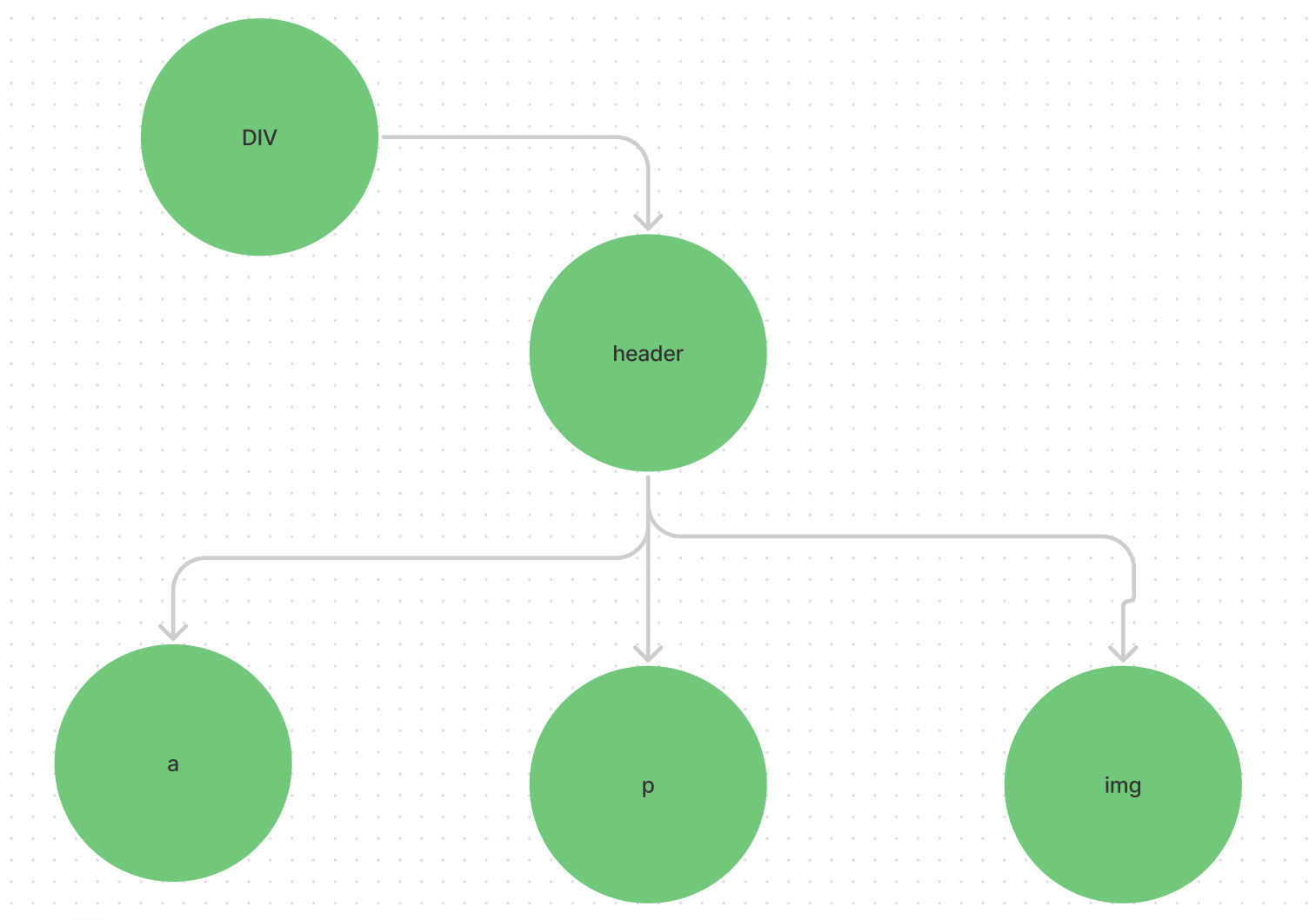
This is what VDOM in react means. Whenever we update a code or state in our code the react will create another dom just like this and check for the changes in the dom. Once the react found out about this change. React will update only that node and its child nodes. In this way, the browser doesn’t need to update the whole dom whenever they react makes a change in the state.
Now you may think that ok, So react will make a node tree and check changes in our node tree and update our code. Then who will React find out state changes in our program right?
React uses listeners to look for changes trigger in our code. This means whenever render function is called or setState is called the listener will notify react that state our program changes need to look for the update in the program.
Even though now we know that changes are notified by listeners how we can execute our code. Code that is not in jsx.
console.log("this is a simple js log")
For that react will use hooks. Like
// hook for running our pure js code
Hook.prototype.hook = function() {
console.log("this is a simple js log")
}
// Connect this hook with the vnode (node on virtaul dom)
We discuss the virtual node and react will target the change by looking at the virtual node. But this is not efficient as possible. We need to make this process efficient. That’s why React uses some methods to update elements.
Whenever there is an update in the virtual dom the react will check the update on the node and find out the node the update happens. But after changing that node it will not look for the child node whether an update happened or not. Instead, it will destroy the child node and create a new only even though there are not many updates on the child node. This is because looking for those changes on the child node and update can increase time consumption.